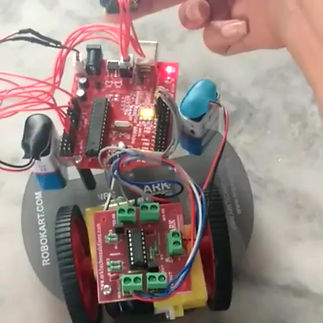
Sovereignty Vehicle
Designed and implemented a gesture-controlled robot with accelerometer fitted on the hand glove to control its motion. Used sensors to detect obstacles, read temperature value, and Bluetooth control
Situation:
Would you like to control your vehicle with hand gestures instead of worrying about your driving tests? Did you know that the gyroscope chip inside your mobile phones which helps the device understand the orientation of the phone and hence a lot of features like auto-rotate and maps are made possible? Let us try to use an accelerometer to control our vehicle.
Task:
The main task here is to first calibrate the values of an accelerometer and then integrate it with an Arduino. So, I first went ahead building a robot vehicle similar to a line follower without an IR sensor and used an accelerometer to control its motion. The accelerometer is attached to our gloves, so that whenever we make a hand gesture, the inclinations of our hand is detected and the vehicle begins to move towards the direction of the inclination of our palm.
Action:
The gesture control robot is simple: the robot car's motion is controlled by the palm's orientation. Obstacle detection, temperature reading, and Bluetooth control were all done via sensors.
You might wonder how it accomplishes this. Let's have a look at it in more detail.
The accelerometer's purpose is straightforward: it detects the wrist's orientation. The accelerometer measures acceleration, which includes gravitational acceleration ('g'). As a result, we may utilize the accelerometer to detect wrist orientation by measuring the component of 'g' in any Arduino MPU-6050 axis.
The X and/or Y axis' angle with vertical varies due to the tilt of the hand, and thus a component of 'g' acceleration operates upon them as well, which may be measured and so displays the hand's orientation.
The Arduino MPU-6050 can measure up to 3g of acceleration and is connected to Arduino via its axis pins, which are connected to Arduino's Analog pins. The voltage values output by the accelerometer is proportional to the acceleration.

Image by Jeremy S. Cook
To add a few more features to the vehicle design and to fancy things up we went ahead plugging in temperature sensor LM35, the Arduino Bluetooth module HC-05 (to make it wirelessly controllable and an ultrasonic sensor to avoid obstacles in front of the bot.
Result:
The results were impresive, the vehicle did move depending upon the hand gestures. The future scope of this project can be to adjust acceleration depending upon the inclination angle so that the sovereignty vehicles can perform well even on rough and uneven terrains.